Next: About this document ...
M3D Stellarator Simulations
H.R. STRAUSS
New York University, New York, NY, USA
L.E. SUGIYAMA
Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA
G.Y. FU, W. PARK, J.BRESLAU, D. MONTICELLO
Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory, Princeton, NJ, USA
M3D code
- Physics
- MHD
- 2 Fluid, neoclassical
- hybrid
- ``artificial sound" for parallel equilibration
- parallelization
- shared memory, OMP
- and distributed memory, MPI
- Mesh
- unstructured mesh of triangles and quadrilaterals in poloidal pl
anes
- 4th order finite differencing or pseudo spectral in the toroidal direction
- initialization
from the VMEC code (working on PIES)
Ideal and Resistive MHD
- Ideal MHD
- ideal
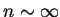
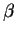 limit is too low.
limit is too low.
- Resistive MHD
- resistive ballooning modes unstable for all
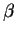 .
.
- Stellarators tend to be resistive interchange unstable, so the resistive
modes are not stabilized at small resistivity, as in tokamaks.
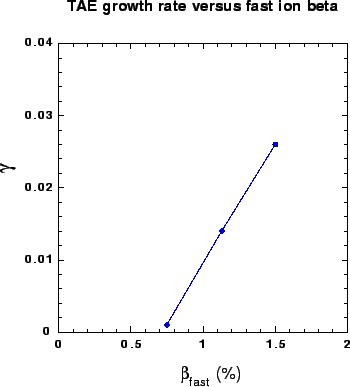
Figure 1:
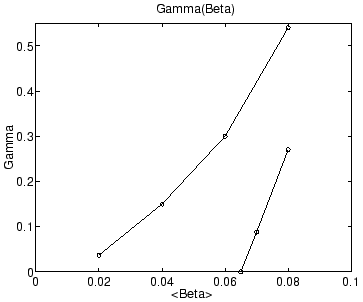
Growth rate 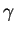 of Ideal and Resistive Mode vs.
of Ideal and Resistive Mode vs. 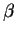
 |
Two fluid
- two fluid
equations (Sugiyama and Park, PoP 2000)
- resistive modes are
stabilized by diamagnetic drifts.
- realistic value of the Hall parameter
- Ideal modes can be stabilized, raising
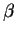 limit.
limit.
Hall parameter
where 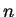 is toroidal mode number.
Ideal modes are stable if
is toroidal mode number.
Ideal modes are stable if
can be stable,
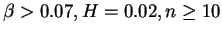
Figure 2:
Electrostatic potential for (a) MHD, 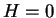 ,
(b) 2 Fluid
,
(b) 2 Fluid 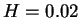 . In both cases,
. In both cases,
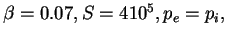 density = constant.
density = constant.
 |
TAE Modes
- Hot particle kinetic effects
can cause TAE modes in stellarators. TAE modes are confirmed
by frequency and linear scaling of growth rate with hot particle
 . The growth rate in a two period stellarator is lower than in
a tokamak with the same profiles and average boundary shaping.
. The growth rate in a two period stellarator is lower than in
a tokamak with the same profiles and average boundary shaping.
Growth rate  vs. hot particle
vs. hot particle  .
Linear relation is characteristic of TAE.
.
Linear relation is characteristic of TAE.
M3D - PIES Comparison
- PIES restart file used to generate M3D input file
- compared vacuum case with islands
Figure 3:
Poincare plots of a test case done with (a) PIES
(b) M3D
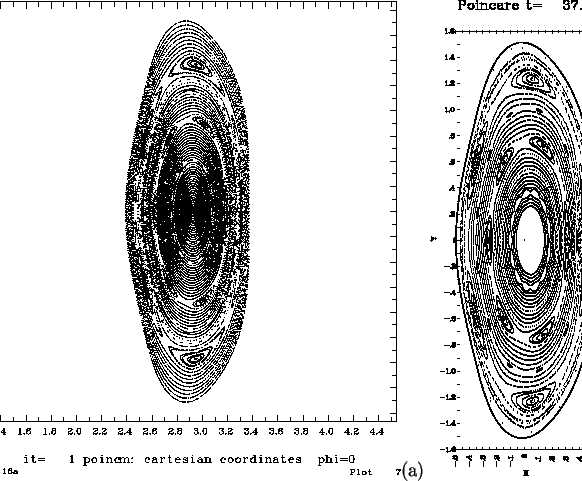 |
Summary
- Two Fluid essential for equilibrium and stability
- Kinetic TAE calculations
- PIES - M3D Comparison
- need to include vacuum region for free boundary computations



Next: About this document ...
Hank Strauss
2003-05-22
 limit is too low.
limit is too low.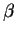 .
.
![]()